How to secure IoT devices and trackers – the complete IoT and GPS security guide
Internet of Things (IoT) devices have taken the world by storm. Our houses are full of such devices as fitness trackers, smartwatches, home security systems, etc. When it comes to businesses, they use several IoT devices, Smart CCTV cameras, smart locking mechanisms, Vehicle trackers, pallet tracking, Bluetooth, and other GPS enabled devices. They may not be computers, smartphones, or tablets, yet they still connect to the Internet. Yet, companies sometimes seem to overlook the security risks associated with such devices.
IoT device security has become more powerful in the recent times. Bluetooth accelerometer manufactured by Shenzhen Eelink Communication Technology Co Ltd sensor is a marvelous piece of IoT. It comes equipped with a temperature sensor, humidity sensor, and accelerometer. It is also a next-generation beacon featuring the latest Bluetooth 5.0 hardware platform. The device is powered by robust intelligence software. This is the best-priced piece of equipment in its class and best suited for small businesses. It is powered by a battery, an active tag, and compatible with the most up to date mobile OS.
Connected IoT devices have become more powerful and gained several capabilities. They may become more attractive targets for malicious actors looking to exploit these at the same time and become targets of malicious attacks. A typical example of IoT devices being a target of DDoS (Denial of Service) attacks may render the IoT device useless. Going forward, the risks involving IoT devices have only turned bigger.
The Federal Trade Commission has, in its releases, asked vendors to build security into their devices on priority.
How to secure IoT devices and trackers in the most efficient manner
Make sure you have the latest firmware – You need to make it a point to check each and every IoT device in your company for the newest firmware. IoT device manufacturers keep a tab on continuing threats to their devices from malicious attacks. They keep pushing over the air updates for their device firmware to improve the devices’ security. In case these updates are not pushed over the air, you need to manually update all your devices. Such updates identify and curtail the ill-effects of device vulnerabilities and exploits. Hence the IoT devices need to be regularly updated. |This process should be automated wherever possible.
Change Default Passwords – Make it a point to change any default passwords that the device may come with. The most common default setting is the device Admin setting, which usually has “Admin” as a username and “Admin” as a password. This can turn into a big weakness for your IoT infrastructure if not dealt with in a timely manner. Ideally, these default passwords should be changed as soon as devices are configured for deployment. Some countries have taken note of this practice of universal passwords. They have made attempts to ban this practice altogether.
Use a secure network – IoT devices are smart by themselves. They would connect to WPA or WPA2 networks for Wi-Fi connections. However, it is your responsibility to ensure that these Wi-Fi and even Bluetooth networks are safe and secure to transmit data. And seepage of data through unsecured Wi-Fi Access Points can lead to data loss or even misuse. You can even change your router names in order to avoid undesirable hacking. Change the default SSID router identifier name. You do not want your router to be broadcasting its manufacturer details like “Huawei” or “NetGear” as this narrows down the hacking tricks for the hacker.
Hiding your SSID will definitely help in increasing security for your IoT devices. It may not be super effective, but it is a first step towards ensuring a secure environment for your IoT devices to function.
Track and assess your devices – Your company should be able to track and identify everything that is connected to your network. If you find an unidentified device, be sure to isolate it and block its network usage. You should also monitor the flow of data traffic on your company network. Assess all devices connected to the network to determine access levels they should ideally be approved for. Keep all devices fully patched and up to date with software updates. When dealing with sensitive data or privacy concerns, it is an effective practice to have a long hard look at your existing IoT devices. The same strategy is effective when applied to the decision to buy a new IoT device. Check which protocols it supports, ease of software patching, etc.
Separate Networks – Within the company, you may opt to have separate networks for separate device sets. E.g. you can have the devices dealing with raw materials on one web and those coping with finished goods on a different network. This helps create working silos and also keeps the rest of the network safe in case of an attack on one section. The use of separate routers is an easy and effective solution in ensuring the security of IoT devices. You may also have a separate network on the same router using different SSIDs.
More IoT device and tracker security tips:
- Older IoT devices should be phased out to be replaced with new and more versions
- Regularly checking privacy and security settings on each of the devices
- Keeping device firmware or software up to date
- Secure authentication processes to be preferred
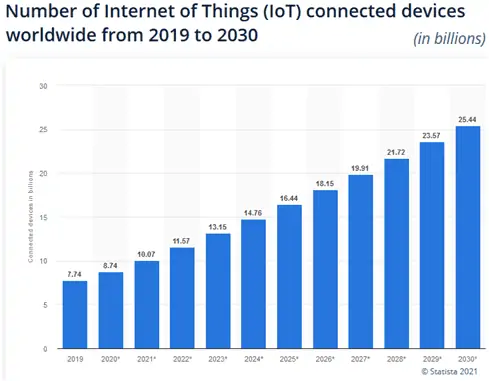
Source: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1183457/iot-connected-devices-worldwide/
Security Laws for IoT Devices
In the United States, California has its own Internet of Things (IoT) Security Law in place. It requires all IoT devices connected over the network to have reasonable security features. The United Kingdom has implemented regulations for the enhancement of security of IoT devices. Australia has introduced a voluntary code of practice that requires IoT device manufacturers to follow the laid-out security principles.
Basically, having a strong password is the best way to boost your company’s IoT devices’ security. It, in a way, also secured other devices on the network. Your IT team, responsible for your IoT devices’ security, may follow the following tips to enhance security.
- Understanding the vital assets and highlight the value of their protection to decision makers in your company
- Develop a central security operation center
- Develop a risk-control team that regularly audits all the IoT devices for compliance with the latest regulations and software vulnerabilities.
- Develop a contingency plan to salvage the attacked IoT devices from the cyber threats
- Develop and implement a threat-intelligence strategy for robust business operations
- Using data analytics to anticipate where and when threats are most likely to occur
- Monitor the system architecture and keep upgrading it to prevent unauthorized access
- Any proliferation in the network can cause a catastrophe. Regular hazard analysis helps in identifying the weakest links in the company’s IT infrastructure. This weak link can pose a threat to the smooth functioning of the rest of the connected devices on the network.
- Understand and put in place a proper governance control across the company
- Create a personal accountability plan
- Detect threats at the earliest, produce relevant reporting, and enable better decision-making, risk management, and business continuity